Front Line Research
An accelerator + "sub" critical reactor = a hybrid nuclear system pursuing safety. Creation of the future energy figure.
Exploration of advanced nuclear systems which researchers around the world compete to develop.
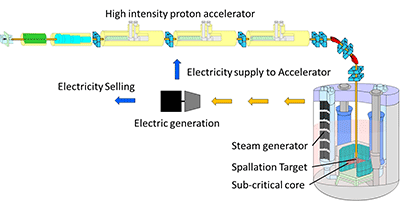
As the best combination of energy sources for the mid-and-long term in our nation, nuclear system (nuclear reactors) is considered as one viable option. The key to further research and development is improvement of long-term safety, and many researchers from Japan and around the world have been promoting various attempts. In which "accelerator driven system (:hereinafter called ADS)" is the center of attention. This is a type of hybrid energy system consisting of the combination of accelerator and nuclear reactor in subcritical states (where nuclear fission chain reaction is less persistent and decrease over time). In this nuclear reactor, high-energy protons accelerated by high-intensity accelerator are injected into a target such as lead-bismuth (Pb-Bi) to induce nuclear spallation reaction, and by irradiating high-energy neutrons produced from this reaction to nuclear reactor care in sub-critical state, nuclear fission reaction is occurred and energy is produced.
ADS relies its sustention of nuclear fission chain reaction on the external accelerator-driven neutron source. If the accelerator is stopped, the nuclear reactor will shut down inevitably without going out of control, making it possible to operate more safely. ADS is also called "nuclear waste incinerator" since it is possible to "transmute (annihilate) nuclear waste".